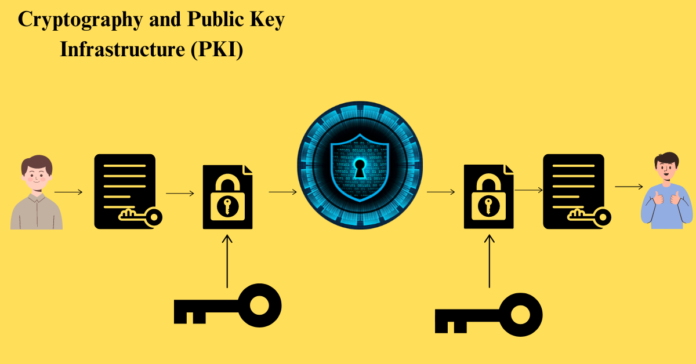
Cryptographic methods play a significant part in defending advanced communications over the endless scene of the web. One of the foundational advances in this space is the Open Key Framework (PKI). In this article, we’ll dig into the basics of cryptography and investigate how PKI functions as a vigorous system for securing and confirming advanced interactions.
What is an Open Key Framework (PKI)?
The Public Key Framework (PKI), in substance, serves as the spine of advanced web security. It envelops a comprehensive suite of apparatuses, conventions, and methods for building up and overseeing open-key encryption. At its center, PKI revolves around the creation, dissemination, administration, capacity, and denial of advanced certificates.
Understanding PKI Components
Certificate Specialist (CA):
The CA is a trusted substance capable of issuing, putting away, and marking advanced certificates. These certificates cryptographically tie open keys with the personalities of clients or devices.
Registration Specialist (RA):
The RA confirms the character of substances by asking for advanced certificates and acting as a middle person between users/devices and the CA.
Certificate Database:
This store stores computerized certificates along with pertinent metadata, counting legitimacy periods.
Central Directory:
A secure store for ordering and putting away cryptographic keys.
Certificate Administration System:
Facilitates the conveyance and gets to the administration of certificates.
Certificate Policy:
Outlines the methods for administering the PKI, guaranteeing straightforwardness and trustworthiness.
How PKI Works
PKI depends on kilter encryption, utilizing a match of keys to open and secure communications and confirm personalities. The open key, disseminated broadly, confirms the sender, whereas the private key, kept private, decodes the message.
PKI Certificates
At the heart of PKI lies belief, epitomized in computerized certificates. These certificates, also known as PKI certificates or X.509 certificates, provide certain verifications of personality. They contain vital data such as the owner’s recognized title, open key, issuance, and termination dates, issuing CA’s subtle elements, and computerized signatures.
Why PKI Matters
PKI finds far-reaching applications, eminently in TLS/SSL conventions, for securing web communications. Site proprietors get computerized certificates from trusted CAs, guaranteeing the genuineness of their online presence. Moreover, PKI encourages mail encryption, archive marking, database security, and more.
Types of Open-Source PKI
- EJBCA Enterprise:Java-based usage is reasonable for enterprise-grade deployments.
- OpenSSL:A flexible toolkit is broadly utilized for PKI-enablement and CA setup.
- CFSSL:Cloudflare’s toolkit for TLS certificate management.
- XiPKI:An adaptable CA and OCSP responder were executed in Java.
- Dogtag Certificate System:An enterprise-class CA supports comprehensive certificate lifecycle management.
Conclusion
In a carefully interconnected world, where security and realness are foremost, an open framework rises as a linchpin innovation. By saddling cryptographic standards with vigorous conventions, PKI not only shields delicate communications but also cultivates belief in the computerized domain. Understanding its complexities enables people and organizations to explore the cyber scene with certainty and resilience.
FAQs
Q: What does PKI do in web security?
A: PKI guarantees secure communication and confirmation online, securing delicate information.
Q: How does PKI confirm certificate authenticity?
A: Trusted Certificate Specialists issue certificates with cryptographic marks, guaranteeing their authenticity.
Q: Where else can PKI be used?
A: PKI expands to mail encryption, report marking, IoT security, and more.
Q: How does PKI handle certificate revocation?
A: PKI employs CRLs or OCSPs to oversee disavowed certificates.
Q: What are the dangers of PKI?
A: Risks incorporate compromised keys and rebel CAs, requiring strong security measures.
Q: What are the choices for PKI?
A: Alternatives incorporate symmetric encryption, blockchain, and decentralized character systems.
Q: How can belief in CAs be ensured?
A: Rely on trustworthy CAs and confirm certifications for trustworthiness.
Q: What role does PKI play in compliance?
A: PKI frequently adjusts to administrative compliance guidelines for information protection.
Q: How do I execute PKI securely?
A: Follow best hones, counting solid key administration and normal audits.
Q: Is PKI appropriate for small businesses?
A: Yes, PKI arrangements cater to businesses of all sizes, upgrading security online.