Nowadays, where connectivity is essential for businesses and individuals alike, ensuring the security of networks is paramount. Network security is the practice and measures to protect a network from unauthorized access, misuse, or disruption. Without adequate security, networks are vulnerable to various threats, including cyberattacks, data breaches, and malware infections. Therefore, understanding the essentials of network security is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining the integrity of network infrastructure.
Understanding Networks

Before delving into network security, it’s essential to grasp the concept of a network itself. Simply put, a network is a collection of interconnected devices, such as computers, servers, routers, and switches, that can communicate with each other and share resources. Networks can be categorized based on their size and scope, ranging from local area networks (LANs) within a single building to wide area networks (WANs) spanning multiple locations. Understanding the components and structure of a network lays the foundation for implementing effective security measures.
Network Monitoring
Network monitoring plays a crucial role in maintaining network bonds. Additionally, it involves continuously monitoring network traffic and activities to detect and respond to potential security threats in real-time. Network administrators can proactively mitigate risks and prevent security breaches by analyzing network traffic patterns and identifying suspicious behavior. Various tools and technologies are available for network monitoring, including intrusion detection systems (IDS), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions.
Types of Network Security
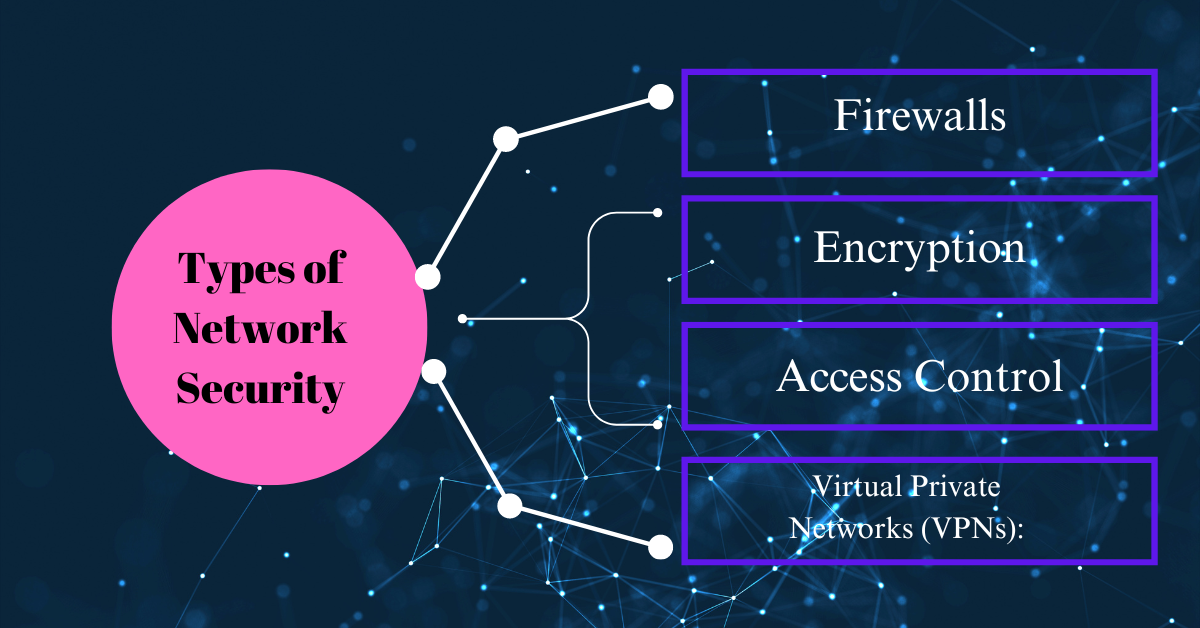
Network security encompasses various measures and technologies designed to protect networks from threats. Some of the main types of network security include:
- Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined rules to prevent unauthorized access.
- Encryption: Encryption involves converting data into a secure format that can only be accessed by authorized parties, ensuring confidentiality and integrity during transmission.
- Access Control: Access control mechanisms restrict access to network resources based on user authentication, authorization, and accountability, preventing unauthorized users from gaining entry.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs create a secure, encrypted connection over a public network, allowing users to access private networks remotely while ensuring confidentiality and privacy.
Network Security Controls
Implementing adequate network bond controls is essential for safeguarding networks against potential threats. Some standard network security controls include:
- User Authentication: Implementing robust authentication methods, such as passwords, biometrics, and multi-factor authentication, to verify the identity of users accessing the network.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Deploying IDS and IPS solutions to detect and block malicious activities and unauthorized access attempts in real time.
- Patch Management: Regularly updating software and firmware to address known vulnerabilities and security weaknesses, reducing the risk of exploitation by attackers.
- Security Policies: Establishing clear and comprehensive security policies and procedures to govern the use of network resources and guide security-related decision-making.
Essential Network Security Tools
Several tools and technologies are available to assist organizations in securing their networks effectively. These include:
- Antivirus Software: Antivirus software detects and removes malware infections, such as viruses, worms, and Trojans, from infected devices to prevent further damage to the network.
- Firewall Solutions: Firewalls filter network traffic based on predefined rules to block unauthorized access and prevent malicious activities from compromising network bonds.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): IDS solutions monitor network traffic for signs of suspicious behavior or potential security breaches, alerting administrators to take appropriate action.
- Encryption Tools: Encryption tools encrypt data to protect it from unauthorized access during transmission and storage, ensuring confidentiality and integrity.
- Vulnerability Scanners: Vulnerability scanners identify weaknesses and vulnerabilities in network infrastructure and applications, allowing organizations to remediate them before attackers can exploit them.
Creating the Right Network Security Mix
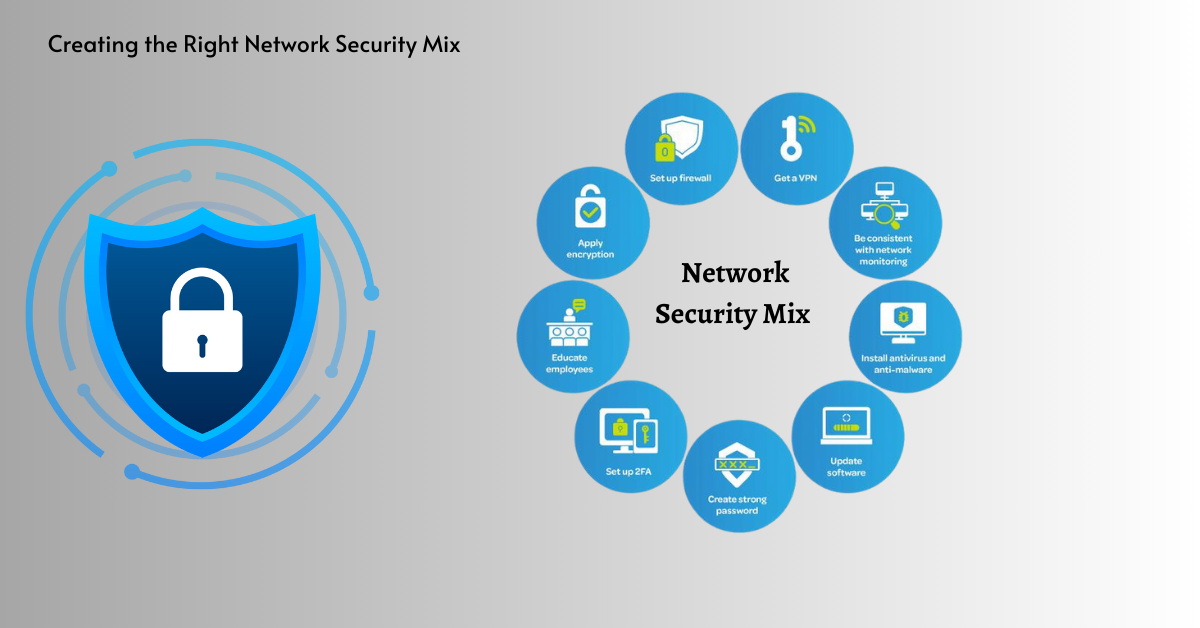
Adequate network bond requires a balanced approach combining multiple security measures and technologies to address various threats and vulnerabilities comprehensively. Organizations should assess their security needs and risks and develop a customized security strategy aligning with their business objectives and regulatory requirements. Organizations can enhance their resilience to evolving cyber threats and protect their networks from potential breaches and attacks by adopting a layered defense approach and regularly reviewing and updating their security posture.
Conclusion
Network security is a critical aspect of modern-day computing, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of network resources and data. By understanding the essentials of network bonds and implementing robust security measures and controls, organizations can mitigate risks, safeguard sensitive information, and maintain the trust and confidence of their stakeholders. With the increasing sophistication and frequency of cyber threats, investing in network security is not just an option but a necessity for businesses and individuals.
FAQs
- Why is network security important?
- Network security is essential because it helps protect sensitive information, prevent unauthorized access, and ensure the integrity and availability of network resources.
- What are the main types of network security?
- The main types of network bonds include firewalls, encryption, access control, and virtual private networks (VPNs).
- What are some standard network security tools?
- Standard network security tools include antivirus software, firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), encryption tools, and vulnerability scanners.
- How can organizations create the right network security mix?
- Organizations can create the right network security mix by assessing their specific security needs and risks, adopting a layered defense approach, and regularly reviewing and updating their security posture.
- What are some best practices for network security?
- Some best practices for network security include implementing robust authentication methods, regularly updating software and firmware, establishing clear security policies, and educating users about security risks and best practices.